The mechanics of the Cosserat media — различия между версиями
Материал из Department of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics
Данил (обсуждение | вклад) |
Данил (обсуждение | вклад) |
||
| Строка 1: | Строка 1: | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
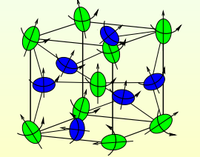
[[Файл:Cosserat.png|thumb|200px| Magnetic materials (Kelvin’s medium — special Cosserat medium with particle posessing large spin)]] | [[Файл:Cosserat.png|thumb|200px| Magnetic materials (Kelvin’s medium — special Cosserat medium with particle posessing large spin)]] | ||
| − | Cosserat medium is a continuum whose point bodies (particles) have rotational degrees of freedom. Examples of Cosserat media: heterogeneous materials with granular structure, composites under loading that causes rotation of (sufficiently rigid) grains (superplastic materials, acoustic metamaterials). | + | Cosserat medium is a continuum whose point bodies (particles) have rotational degrees of freedom. Examples of Cosserat media: heterogeneous materials with granular structure, composites under loading that causes rotation of (sufficiently rigid) grains (superplastic materials, acoustic metamaterials). Cosserat medium is a particular case of complex medium. Its point-body is rigid. There are other more complex media, e.g. where a point-body is deformable (protein chains, porous media, etc.) It is only a first step to the world of enriched continua. |
Версия 23:17, 11 января 2015
Introduction
Cosserat medium is a continuum whose point bodies (particles) have rotational degrees of freedom. Examples of Cosserat media: heterogeneous materials with granular structure, composites under loading that causes rotation of (sufficiently rigid) grains (superplastic materials, acoustic metamaterials). Cosserat medium is a particular case of complex medium. Its point-body is rigid. There are other more complex media, e.g. where a point-body is deformable (protein chains, porous media, etc.) It is only a first step to the world of enriched continua.