Эллиптический маятник — различия между версиями
Павел (обсуждение | вклад) (→Решение частного случая) |
Павел (обсуждение | вклад) (→Решение) |
||
| (не показано 17 промежуточных версий этого же участника) | |||
| Строка 1: | Строка 1: | ||
'''''Задача:''''' С помощью языка программирования JavaScript смоделировать эллиптический маятник. | '''''Задача:''''' С помощью языка программирования JavaScript смоделировать эллиптический маятник. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Исполнитель:''' [[Булдаков Павел]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Группа:''' [[Группа 09|09]] (23604) | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Семестр:''' весна 2015 | ||
| + | |||
[[Файл:maytnic.png|thumb|]] | [[Файл:maytnic.png|thumb|]] | ||
== Решение == | == Решение == | ||
| − | {{#widget:Iframe |url=http://tm.spbstu.ru/htmlets/buldakov/4.html |width= | + | {{#widget:Iframe |url=http://tm.spbstu.ru/htmlets/buldakov/4.html |width=1200 |height=600}} |
| Строка 11: | Строка 18: | ||
<div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed"> | ||
'''Текст программы на языке JavaScript:''' <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | '''Текст программы на языке JavaScript:''' <div class="mw-collapsible-content"> | ||
| − | + | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="javascript" line start="1" enclose="div"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="javascript" line start="1" enclose="div"> | ||
function main() | function main() | ||
| Строка 229: | Строка 236: | ||
<math>T = \frac{1}{2} \ (m_1 + m_2) \dot y^{2} + \frac{1}{2} \ m_2 \ l ^{2} \dot \varphi^{2} + m_2 \ l\dot y\dot \varphi \cos(\varphi )\</math> | <math>T = \frac{1}{2} \ (m_1 + m_2) \dot y^{2} + \frac{1}{2} \ m_2 \ l ^{2} \dot \varphi^{2} + m_2 \ l\dot y\dot \varphi \cos(\varphi )\</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\Pi = - m_2 \ l\ g \cos(\varphi )\ </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>L = \frac{1}{2} \ (m_1 + m_2) \dot y^{2} + \frac{1}{2} \ m_2 \ l ^{2} \dot \varphi^{2} + m_2 \ l\ (\dot y\dot \varphi + g) \cos(\varphi )\</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{\partial L}{\partial\dot y} = (m_1 + m_2) \dot y + m_2 \ l\dot \varphi \cos(\varphi )\</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{\partial L}{\partial y} = 0 </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{\partial L}{\partial\dot \varphi } = m_2 \ l ^{2} \dot \varphi + m_2 \ l\dot y \cos(\varphi )\</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{\partial L}{\partial\varphi} = - m_2 \ l\ (\dot y\dot \varphi + g) \sin(\varphi )\</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | В результате получаем уравнения , описывающие движение рассматриваемой системы : | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> (m_1 + m_2) \ddot y + m_2 \ l\ddot \varphi \cos(\varphi ) - m_2 \ l\dot \varphi \sin(\varphi ) = 0</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math> l \ddot \varphi + \ddot y \cos(\varphi ) + g \sin(\varphi) = 0 </math> | ||
== См. также == | == См. также == | ||
Текущая версия на 02:10, 27 мая 2015
Задача: С помощью языка программирования JavaScript смоделировать эллиптический маятник.
Исполнитель: Булдаков Павел
Группа: 09 (23604)
Семестр: весна 2015
Содержание
Решение[править]
Программа: скачать
1 function main()
2 {
3 //определяем сцену
4
5 var scene = new THREE.Scene();
6 var camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(45, window.innerWidth/window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000);
7 var render = new THREE.WebGLRenderer();
8 render.setClearColor(0xEEEEEE, 1);
9 render.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight);
10
11 //ставим оси
12
13 var axes = new THREE.AxisHelper(20);
14 scene.add(axes);
15 var planeGeometry = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(80,10,1,1);
16 var planeMaterial = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({color:0xCCCCCC});
17 var plane = new THREE.Mesh(planeGeometry, planeMaterial);
18 plane.rotation.x = -0.5*Math.PI;
19 plane.position.x=0;
20 plane.position.y=0;
21 plane.position.z=0;
22 scene.add(plane);
23
24 //создаем ползун
25
26 var cubeGeometry = new THREE.CubeGeometry(20,10,10);
27 var cubeMesh = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({color:0xff0000, wireframe:false});
28 var cube = new THREE.Mesh(cubeGeometry, cubeMesh);
29 cube.position.x=-30;
30 cube.position.y=5;
31 cube.position.z=0;
32 scene.add(cube);
33
34 // создаем соединяющую
35
36 var cube1Geometry = new THREE.CubeGeometry(1,15,0.5);
37 var cube1Mesh = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({color:777777, wireframe:false});
38 var cube1 = new THREE.Mesh(cube1Geometry, cube1Mesh);
39 cube1.position.x=-20;
40 cube1.position.y=-5;
41 cube1.position.z=5;
42 scene.add(cube1);
43
44 // создаем шшар
45
46 var trajectoryGeometry = new THREE.SphereGeometry(0.3,20,20);
47 var trajectoryMaterial = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({color:0x7777ff, wireframe:true});
48 var sphereGeometry = new THREE.SphereGeometry(4,20,20);
49 var sphereMaterial = new THREE.MeshLambertMaterial({color:0x7777ff, wireframe:false});
50 var sphere = new THREE.Mesh(sphereGeometry, sphereMaterial)
51 sphere.position.x=-30;
52 sphere.position.y=-15;
53 sphere.position.z=5;
54 scene.add(sphere);
55
56 // устанавливаем источник света
57
58 var spotLight = new THREE.SpotLight(0xffffff);
59 spotLight.position.set(-40,60,100);
60 scene.add(spotLight);
61
62 //задаем тени
63
64 render.shadowMapEnabled = true;
65 plane.receiveShadow = true;
66 cube.castShadow = true;
67 sphere.castShadow = true;
68 spotLight.castShadow = true;
69
70
71 //задаем положение камеры
72
73 camera.position.x= 1.5;
74 camera.position.y= 13.7;
75 camera.position.z= 80;
76 camera.lookAt(scene.position);
77 $("#webGL").append(render.domElement);
78
79 //добавляем ползунки для изменения скорости , массы, длины и g
80
81
82 var controls = new function() {
83 this.m1 = 7.4;
84 this.m2 = 2.9;
85 this.l = 1;
86 this.g = 9.83
87 this.bouncingSpeed = 0.03;
88 }
89 var gui = new dat.GUI();
90
91 gui.add(controls, 'bouncingSpeed',0,0.5);
92 gui.add(controls, 'm1',1,10);
93 gui.add(controls, 'm2',1,10);
94 gui.add(controls, 'l',0.5,5);
95 gui.add(controls, 'g',0.5,20);
96
97
98
99 var stats = initStats();
100 var step = 0;
101
102 contra = new THREE.OrbitControls(camera);
103 contra.dumping = 0.2;
104
105
106 window.addEventListener('resize',onWindowResize,false);
107
108 function onWindowResize(){
109 camera.aspect = window.innerWidth/window.innerHeight;
110 camera.updateProjectionMatrix();
111 render.setSize(window.innerWidth,window.innerHeight);
112 renderer();
113 }
114
115 renderer();
116
117 // функция, в которой задаются законы, по которым работает эллиптический маятник
118
119 function renderer()
120 {
121
122
123 stats.update();
124
125 step+=controls.bouncingSpeed;
126 cube1.scale.set(1,controls.l,0.5);
127 t = 15*controls.l;
128
129 k =Math.sqrt(controls.g/t*controls.m1/(controls.m1+controls.m2));
130 a = t*controls.m1/(controls.m1+controls.m2)*controls.m2/controls.m1*controls.g;
131 cube.position.x=-a*Math.sin(k*step);
132 sphere.position.x = t*(Math.sin(Math.sin(k*step))) - a*Math.sin(k*step);
133 sphere.position.y =-t*(Math.cos(Math.sin(k*step)));
134 cube1.position.x=(cube.position.x + sphere.position.x)/2;
135 cube1.position.y=-t*(Math.cos(Math.sin(k*step)))/2;
136 u = (-cube.position.x + sphere.position.x)/2;
137 v = sphere.position.y/2;
138 cube1.rotation.z=Math.asin(u/Math.sqrt(v*v + u*u));
139
140
141
142 requestAnimationFrame(renderer);
143 contra.update();
144 render.render(scene,camera);
145
146 var trajectory = new THREE.Mesh(trajectoryGeometry,trajectoryMaterial);
147 trajectory.position.x = sphere.position.x;
148 trajectory.position.y = sphere.position.y;
149 trajectory.position.z = 5;
150 scene.add(trajectory);
151 document.getElementById("td1").innerHTML = camera.position.x;
152 document.getElementById("td2").innerHTML = camera.position.y;
153 document.getElementById("td3").innerHTML = camera.position.z;
154
155 }
156
157
158 }
159 function initStats()
160 {
161 var stats = new Stats();
162 stats.setMode(0);
163 stats.domElement.style.position='absolute';
164 stats.domElement.style.left = '0px';
165 stats.domElement.style.top = '0px';
166 $("#Stats").append(stats.domElement);
167 return stats;
168 }
Используемые библиотеки[править]
- cloudflare.js
- dat.gui.js
- googleapis.js
- orbitControls.js
- stats.js
- trackballControls.js
Возможности программы[править]
- задание скорости раскачивания маятника
- изменение масс шара и ползуна
- изменения силы тяжести
- детальное рассмотрение работы с удобного ракурса
- получение рисунка траектории маятника
Решение частного случая[править]
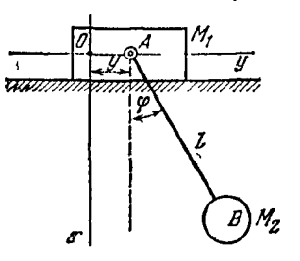
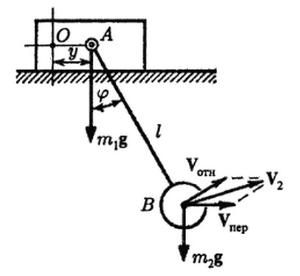
Условия задачи:
Составить уравнения движения эллиптического маятника, состоящего из ползуна M1 массы m1, скользящего без трения по горизонтальной плоскости, и шарика M2 массы m2, соединенного с ползуном стержнем AB длины l. Стержень может вращаться вокруг оси A, связанной с ползуном и перпендикулярной плоскости рисунка. Массой стержня пренебречь.
Решение:
где - функция Лагранжа
- кинетическая энергия системы, - потенциальная энергия системы ,
, где - кинетическая энергия ползуна, - кинетическая энергия шара
, ,
В результате получаем уравнения , описывающие движение рассматриваемой системы :